Culture/Human Beings

Technology/
Media
|
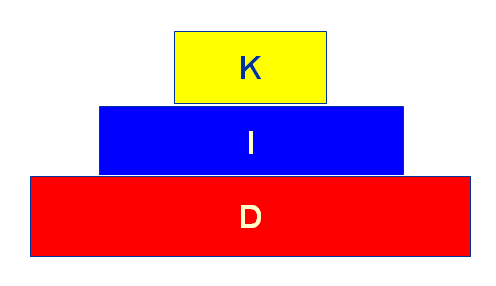 |
Knowledge: tacit, relationships, incentives, policies, not “reinventing the wheel”, continuing education, communication and cultural barriers, tracking work flow
Information: access, authentication and version control, information retrieval systems, indexing, metadata, architecture, interface, design, data mining
Data: collection, preservation, integrity, migration, compatibility
|
|
|
How does one measure the value of a law firm? Not by the real estate, equipment or other tangible assets it owns. . . . Not by its individual lawyers -- they are constantly leaving or retiring, and new ones (hopefully) are constantly being added. Not even by its client roster. . . . Instead, the true value of a law firm is in its collective knowledge. Knowledge of the law, knowledge of its capabilities, knowledge of its client needs and of its competitors. A firm's effectiveness turns on how well its lawyers can bring their collective knowledge to bear in their client's behalf and how well the firm can use this knowledge to market its services. Rovner, J.R.(1999). Building the Smart Law Firm: Guidelines for Effective Management of Legal Knowledge Management.
In Daily Journal Legal Works, The Technology Answer Show, Los Angeles 1999, Conference and Exhibition (pp. 133-138) Little Falls, NJ: Glasner Legal Works.
|
“The only sustainable advantage a firm has comes from what it collectively knows, how efficiently it uses what it knows, and how readily it acquires and uses new knowledge.”
Thomas Davenport and Laurence Prusak, cited in Matthew Parsons, Effective Knowledge Management for Law Firms, 4 (Oxford University Press, 2004)
|